These forced-vortex units process dry materials to exceptional fineness and uniformity over a wide range of feed variations. They can operate either in closed-circuit within a conventional air-swept milling system or as an independent, “stand-alone” system incorporating feeder, fan and product collection equipment. The SPAX can be installed in existing air systems with a minimum of modification and will accurately separate products of exceptional fineness over a wide range of feed variations.
Features and benefits:
-
Operating particle size range of 1 to 150 microns
-
Excellent sharpness of cut
-
Precise on-stream control of cut-point by variation of rotor speed
-
Reduced power consumption due to low system resistance
-
Adjustable secondary air system for optimization of classification efficiency
-
Operates under negative pressure promoting dust-free environment
-
Robust construction and build quality for long service life
-
Mild steel, stainless steel
-
Available in different sizes for throughputs from 100 kg/h to 10 t/h.
-
Easy access for cleaning and maintenance through inspection doors
Optional Extras
-
Ceramic rotors
-
Abrasion-resistant steel and rubber, polyurethane or ceramic lining
Working Principle
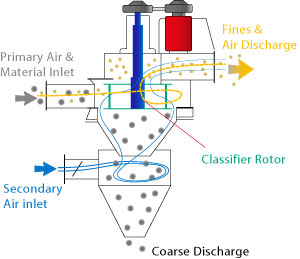
Air Classifiers separate particles based on the opposing principles of centrifugal force and aerodynamic drag force. Feed material is conveyed with the main supply of air to the spiral housing. Due to the shape of the housing and the rotation of the separating rotor, a spiral current is created, in which the material to be classified is separated into two fractions, fine and coarse material. The fine material is sucked inwards through the rotor and leaves the classifier along with the air.
The coarse material is hurled by centrifugal force against the housing wall and falls downward. A secondary air inlet introduces a controllable amount of air that moves upward into the classification zone, increasing the residence time of agglomerated particles. This air helps to increase efficiency for smaller cut-points. Product is then discharged through a rotary air lock. Cut size can be set within the range of 1 to 150 µm by variation of rotor speed as well as primary and secondary air volume. |
 |
Typical Applications:
Aluminum Hydroxide, Aluminum Oxide, Aluminum Powder, Barite, Bentonite, Calcium, Cement, Chalk, Clay, Cocoa Powder, Coconut Shell Meal, Coke, Copper Powder, Dextrose, Dolomite, Enzymes, Glimmer, Graphite, Gypsum, Iron Oxide, Kaolin, Lactose, Limestone, Magnesium Oxide, Maize Flour, Manganese Dioxide, Methylcellulose, Phosphates, Pigments, Polyamide, Pot ash, Proteins, PVC Powder, Resins, Silica, Silicates, Soya Flour, Starch, Sugar, Tobacco Dust, Zinc Dust, ...

